The Role of Beamforming and AESA Antennas in SATCOM
Advancements in Satellite Communication Technologies
The advancement of satellite communication technologies has revolutionized how we transmit and receive information across the globe. One of the most significant developments in this field is the integration of beamforming and active electronically scanned array (AESA) antennas. These technologies have transformed satellite communication (SATCOM) by enhancing signal quality, network efficiency, and spectrum utilization, making them indispensable in modern telecommunications, scientific research, national security, and beyond.
Understanding Beamforming
Beamforming is a sophisticated signal processing technique employed in antenna arrays to direct signals toward specific locations rather than broadcasting them indiscriminately. This capability significantly improves signal strength while minimizing interference, making communication systems more efficient. When combined with multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) and AESA technologies, beamforming becomes a foundational component of modern wireless networks, including mobile communications, Wi-Fi, and radar applications.
The Role of AESA Antennas
AESA antennas, also referred to as phased array antennas, consist of multiple stationary elements that work in unison to transmit and receive signals. These antennas steer beams electronically using integrated circuits at each radiating element, eliminating the need for mechanical movement. This design offers several advantages, including a soft failure mechanism that ensures performance remains largely unaffected even if some elements fail. AESA antennas also enable rapid beam steering in microseconds and can support multiple independently steerable beams, enhancing overall system performance. Their low-profile, mechanically robust design further improves reliability, while their ability to steer nulls and suppress interference makes them valuable in security-sensitive applications.
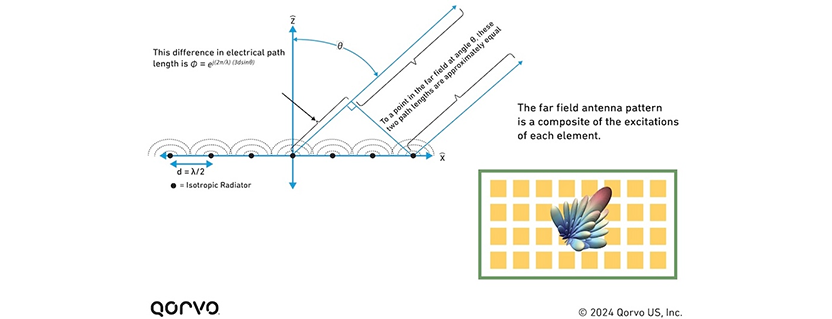
 Figure 1: Simplified one-dimensional planar array antenna with a row of isotropic radiators.
Figure 1: Simplified one-dimensional planar array antenna with a row of isotropic radiators.
Operating at Millimeter-Wave Frequencies
Operating at millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies such as 24, 26, 28, 37, or 39 GHz, AESA antennas produce highly directive beams. These focused beams counteract high path loss, allowing for effective long-range communications. They also facilitate spatial diversity, where multiple beams reuse the same frequency spectrum, thereby increasing system capacity without additional bandwidth consumption.
Types of Beamforming Architectures
Beamforming architectures can be categorized into three main types: analog, digital, and hybrid. Each approach offers distinct advantages and trade-offs. Analog beamforming uses phase shifters to adjust signal directionality before transmission, making it a cost-effective solution that minimizes power consumption. However, it only supports a single beam per antenna array, limiting its flexibility. Digital beamforming, on the other hand, allows for dynamic control by processing signals at each antenna element. This method supports multiple simultaneous beams, offering enhanced performance but requiring greater power and computational resources. Hybrid beamforming combines both analog and digital techniques, dividing the antenna array into sub-arrays, each controlled by an analog beamforming network. Digital processing further refines the beam direction, striking a balance between cost, power efficiency, and performance.
Addressing Beam Squinting with Time-Delay Units (TDUs)
One of the primary challenges in beamforming is beam squinting, a phenomenon where phase shifters introduce inaccuracies at different frequencies. This issue arises because phase shifters maintain a constant phase shift across frequencies, causing the beam to steer at slightly different angles as frequency changes. Time-delay units (TDUs) offer a solution by maintaining a consistent phase slope over a frequency range, effectively eliminating beam squinting. Engineers working on broadband systems often use a combination of phase shifters and TDUs to optimize performance and minimize signal distortion.
 Figure 2: Beam squinting/distortion
Figure 2: Beam squinting/distortion
Beamforming in SATCOM and 5G Networks
The adoption of beamforming in SATCOM and 5G networks is accelerating due to its ability to enhance data throughput, improve signal-to-noise ratio, increase spectral efficiency, and enable smart connectivity. Higher bandwidth utilization allows for improved transmission rates, while focused beams minimize interference, ensuring better performance. The ability to reuse frequencies within a given area maximizes spectrum utilization, which is crucial in an era of increasing data demand. By dynamically adjusting beams, these networks can optimize signal coverage and ensure efficient communication even in challenging environments.
Applications of Beamforming and AESA Antennas
Satellite Communications (SATCOM)
Beamforming plays a critical role in satellite communications by enabling precise beam steering, interference mitigation, and multi-beam operations. These capabilities enhance connectivity in remote areas, improve broadband access for aviation and maritime applications, and provide secure communication for military operations.
5G Networks
In 5G networks, beamforming helps overcome propagation challenges, ensuring reliable, high-speed connectivity by directing signals to specific users rather than broadcasting across a wide area. This targeted approach significantly reduces interference and improves bandwidth efficiency.
Radar and Aerospace
Beyond telecommunications, AESA antennas and beamforming are extensively utilized in radar and aerospace applications. Radar systems benefit from enhanced resolution and detection range, as AESA antennas can rapidly adjust their beams without mechanical movement. This capability is particularly valuable in defense and surveillance, where precise object tracking and rapid response times are critical. In aerospace applications, these technologies enable more reliable and efficient communication links between aircraft and ground stations, improving overall situational awareness and operational effectiveness.
Future Developments in Beamforming and AESA Technologies
As beamforming and AESA technologies continue to evolve, future advancements will focus on higher integration, AI-powered optimization, and post-quantum security. The development of more compact and efficient beamforming integrated circuits (ICs) will allow for miniaturized, high-performance antenna arrays suitable for a wide range of applications. Machine learning algorithms will enhance beam-steering precision and dynamic network management, further improving efficiency and adaptability. Additionally, advancements in encryption methods will secure satellite communications against emerging cyber threats, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality in an increasingly connected world.
Conclusion
The integration of beamforming and AESA antennas into SATCOM and wireless networks marks a significant step forward in communication technology. By improving signal quality, network efficiency, and spectrum utilization, these technologies address the growing demand for high-speed, reliable wireless connectivity. As research and development continue, the future of satellite and wireless communications will be defined by even more advanced and efficient implementations of these groundbreaking technologies.
Get in touch for orders or any queries: sales@rfdesign.co.za / +27 21 555 8400
Courtesy of everythingRF